Ferrous sulfate, dried
Ferrous sulfate, dried
Ferrous sulfate
(FAIR-us SUL-fayt)
Fe50
Feosol
Feratab
Slow FE (OTC)
Classification:
Antianemic, iron
Action/Kinetics:
The normal daily iron intake for males is 12-20 mg and for females is 8-15 mg, although only about 10% (1-2 mg) of this iron is absorbed. Iron is absorbed from the duodenum and upper jejunum by an active mechanism through the mucosal cells where it combines with the protein transferrin. Iron is stored in the body as hemosiderin or aggregated ferritin which is found in reticuloendothelial cells of the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. About two-thirds of total body iron is in the circulating RBCs in hemoglobin. Absorption is enhanced when stored iron is depleted or when erythropoesis occurs at an increased rate. Food decreases iron absorption by up to two-thirds. The daily loss of iron through urine, sweat, and sloughing of intestinal mucosal cells is 0.5-1 mg in healthy men; in menstruating women, 1-2 mg is the normal daily loss. Least expensive, most effective iron salt for PO therapy. Ferrous sulfate products contain 20% elemental iron, whereas ferrous sulfate dried products contain 30% elemental iron. The exsiccated form is more stable in air.
Uses:
Prophylaxis and treatment of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemias. Dietary supplement for iron. Optimum therapeutic responses are usually noted within 2-4 weeks. Investigational: Clients receiving epoetin therapy (failure to give iron supplements either IV or PO can impair the hematologic response to epoetin).
Contraindications:
Hemosiderosis, hemochromatosis, peptic ulcer, regional enteritis, and ulcerative colitis. Hemolytic anemia, pyridoxine-responsive anemia, and cirrhosis of the liver. Use in those with normal iron balance.
Special Concerns:
Allergic reactions may result due to certain products containing tartrazine and some products containing sulfites.
Side Effects:
GI: Constipation, gastric irritation, nausea, abdominal cramps, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, dark-colored stools. These effects may be minimized by administering preparations as a coated tablet. Soluble iron preparations may stain the teeth.
Laboratory Test Alterations:
Iron may affect electrolyte balance determinations.
Overdose Management:
Symptoms: Symptoms occur in four stages--(1) Lethargy, N&V;, abdominal pain, weak and rapid pulse, tarry stools, dehydration, acidosis, hypotension, and coma within 1-6 hr. (2) If client survives, symptoms subside for about 24 hr. (3) Within 24-48 hr symptoms return with diffuse vascular congestion, shock, pulmonary edema, acidosis, seizures, anuria, hyperthermia, and death. (4) If client survives, pyloric or antral stenosis, hepatic cirrhosis, and CNS damage are seen within 2-6 weeks. Toxic reactions are more likely to occur after parenteral administration.Treatment (Iron Toxicity):
- General supportive measures.
- Maintain a patent airway, respiration, and circulation.
- Induce vomiting with syrup of ipecac followed by gastric lavage using tepid water or 1%-5% sodium bicarbonate (to convert from ferrous sulfate to ferrous carbonate, which is poorly absorbed and less irritating). Saline cathartics can also be used.
- Deferoxamine is indicated for clients with serum iron levels greater than 300 mg/dL. Deferoxamine is usually given IM, but in severe cases of poisoning it may be given IV. Hydration should be maintained.
- It may be necessary to treat for shock, acidosis, renal failure, and seizures.
Drug Interactions:
- Antacids, oral /
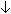 Iron absorption from GI tract
Iron absorption from GI tract
- Ascorbic acid / Ascorbic acid, 200 mg or more,
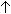 iron absorption
iron absorption
- Chloramphenicol /
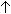 Serum iron levels
Serum iron levels
- Cholestyramine /
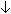 Iron absoprtion from GI tract
Iron absoprtion from GI tract
- Cimetidine /
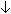 Iron absorption from GI tract
Iron absorption from GI tract
- Fluoroquinolones /
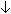 Fluoroquinolone absorption from GI tract R/T formation of a ferric ion-quinolone complex
Fluoroquinolone absorption from GI tract R/T formation of a ferric ion-quinolone complex
- Levodopa /
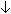 Levodopa absorption R/T formation of chelates with iron salts
Levodopa absorption R/T formation of chelates with iron salts
- Levothyroxine /
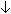 Levothyroxine efficacy
Levothyroxine efficacy
- Methyldopa /
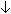 Methyldopa absorption from GI tract
Methyldopa absorption from GI tract
- Pancreatic extracts /
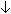 Iron absorption from GI tract
Iron absorption from GI tract
- Penicillamine /
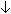 Penicillamine absorption from GI tract due to chelation
Penicillamine absorption from GI tract due to chelation
- St. John's wort / May
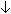 absorption of iron
absorption of iron
- Tetracyclines /
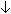 Absorption of both tetracyclines and iron from GI tract
Absorption of both tetracyclines and iron from GI tract
- Vitamin E /
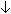 Response to iron therapy
Response to iron therapy
How Supplied:
Ferrous sulfate: Capsule: 250 mg, 324 mg; Capsule, Extended Release: 250 mg; Elixir: 220 mg/5 mL; Enteric Coated Tablet: 325 mg; Liquid: 25 mg/mL, 75 mg/0.6 mL, 300 mg/5 mL; Solution: 300 mg/5 mL; Syrup: 90 mg/5 mL; Tablet: 195 mg, 300 mg, 324 mg, 325 mg; Tablet, Extended Release: 250 mg, 525 mg Ferrous sulfate, dried: Capsule, Extended Release: 150 mg, 159 mg; Enteric Coated Tablet: 200 mg; Tablet: 200 mg; Tablet, Extended Release: 152 mg, 159 mg, 160 mg
Dosage
Ferrous Sulfate
•Extended-Release Capsules
Adults: 150-250 mg 1-2 times/day. This dosage form is not recommended for children.
•Elixir, Oral Solution, Tablets, Enteric-coated Tablets
Prophylaxis.
Adults: 300 mg/day. Pediatric: 5 mg/kg/day.
Anemia.
Adults: 300 mg b.i.d. increased to 300 mg q.i.d. as needed and tolerated. Pediatric: 10 mg/kg t.i.d. The enteric-coated tablets are not recommended for use in children.
•Extended-Release Tablets
Adults: 525 mg 1-2 times/day. This dosage form is not recommended for use in children.
Ferrous Sulfate, Dried
•Capsules
Prophylaxis.
Adults: 300 mg/day. Pediatric: 5 mg/kg/day.
Anemia.
Adults: 300 mg b.i.d. up to 300 mg q.i.d. as needed and tolerated. Pediatric: 10 mg/kg t.i.d.
•Tablets
Prophylaxis.
Adults: 200 mg/day. Pediatric: 5 mg/kg/day.
Anemia.
Adults: 200 mg t.i.d. up to 200 mg q.i.d. as needed and tolerated. Pediatric: 10 mg/kg t.i.d.
•Extended-Release Tablets
Adults: 160 mg 1-2 times/day. This dosage form is not recommended for use in children.